
Loading...


Loading...


Strong encryption protects sensitive communications and stored data.
Strong encryption protects you when you use a smartphone, browse the web, bank online, or send electronic messages to your family and colleagues.
Encryption can also help authenticate your credentials, preventing criminals from impersonating you, viewing your email and photos, or accessing your bank accounts and health data.
Encryption is a mathematical process that scrambles information; it is often used to secure or authenticate sensitive documents. Each use of encryption generates a very long number that is the mathematical solution to the formula and can unscramble the protected sensitive information. This "key" must be kept a secret or anyone who has it will be able to access the information.


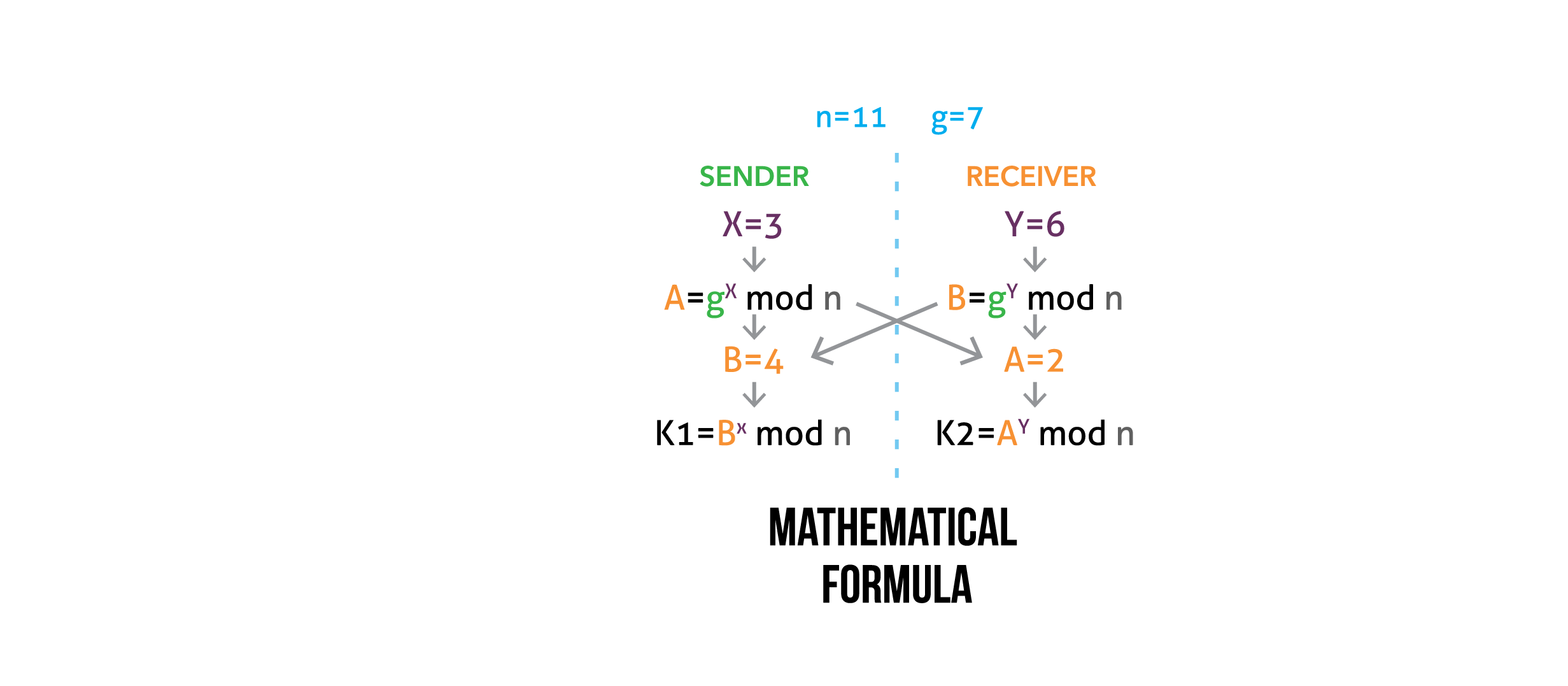

Click through the tabs to explore the benefits of encryption and the risks of weakening encryption.
Encryption protects you everywhere.
Every day, encryption protects confidential business data, individuals’ communications, and sensitive government records.
Protecting documents and photos stored in the cloud from access and publication.
Preventing blackmailers from cryptowalling medical systems.
Ensuring that criminals cannot modify clocks to manipulate financial transactions or security measures.
Preventing hackers from remotely controlling or stalling cars.
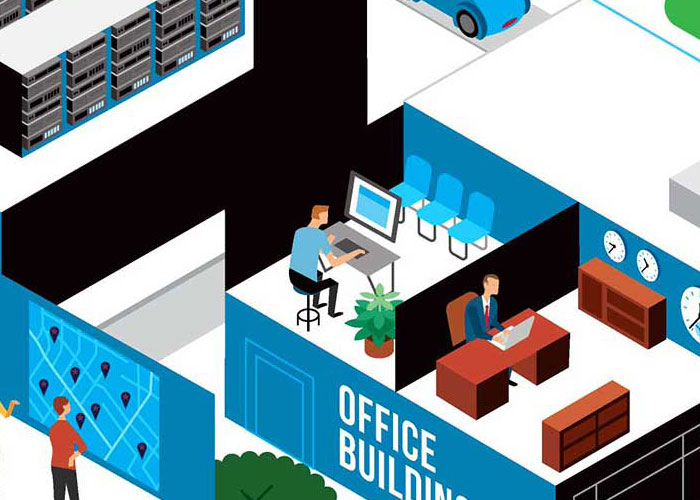
Protecting location data about delivery companies’ customers and workers.
Preventing criminals from intercepting and leaking company communications.
Protecting SSNs and credit profiles from identity thieves.
Preventing hackers from stealing trade secrets and selling info to competing companies and nations.
Preventing malware from stealing banking app credentials.
Preventing interception of sensitive health information.
Preventing thieves from skimming credit card information.
Protecting misplaced laptops from unauthorized access by identity thieves.
Preventing apps from leaking personal health information.
Preventing attackers from commanding insulin pumps to administer an overdose.
Preventing criminals from breaching school systems, imperiling school funding, and exposing children’s data.
Preventing foreign adversaries from stealing sensitive military technologies.
Protecting overseas troops from foreign surveillance and targeted assaults.
Preventing criminals from modifying voter registrations and votes.
Protecting sensitive government personnel data about trusted officials.
Protecting lawmakers’ and candidates’ emails from leaks and forgery.
Preventing foreign adversaries from accessing and mapping critical infrastructure.
Protecting SCADA systems from unauthorized control and preventing service disruptions and injuries.
Protecting nuclear centrifuge equipment from computer viruses and foreign control.
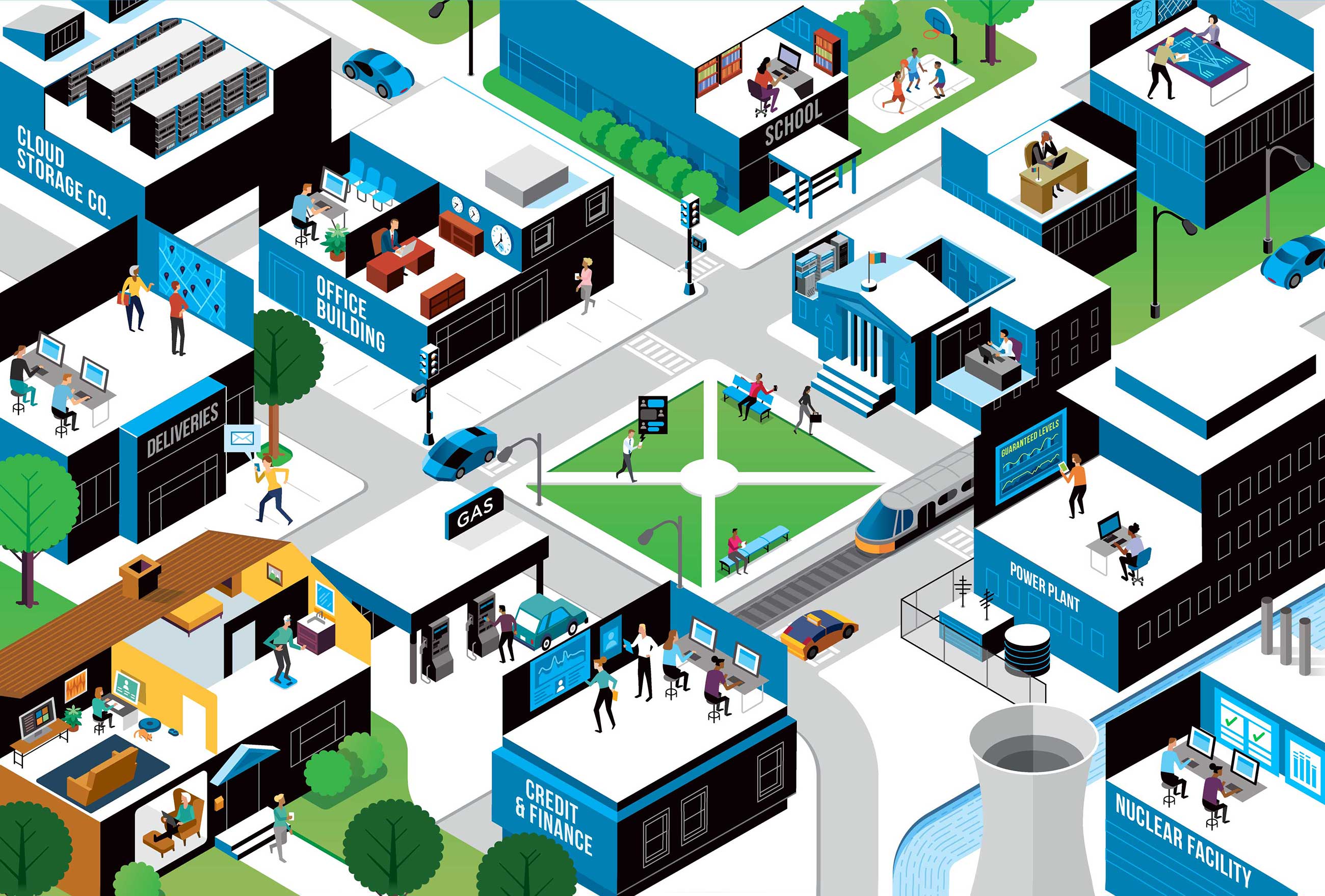

Click the labels above to see how encryption protects data and how bad actors can misuse unencrypted information.
Protecting documents and photos stored in the cloud from access and publication.

Preventing blackmailers from cryptowalling medical systems.

Ensuring that criminals cannot modify clocks to manipulate financial transactions or security measures.
Preventing hackers from remotely controlling or stalling cars.

Protecting location data about delivery companies’ customers and workers.

Preventing criminals from intercepting and leaking company communications.
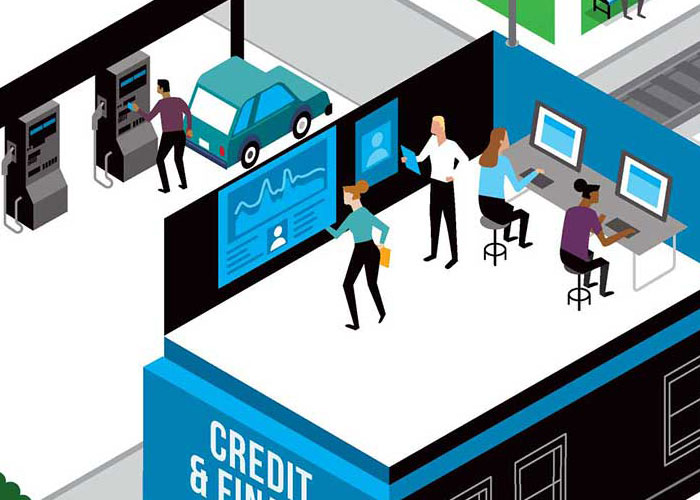

Protecting SSNs and credit profiles from identity thieves.
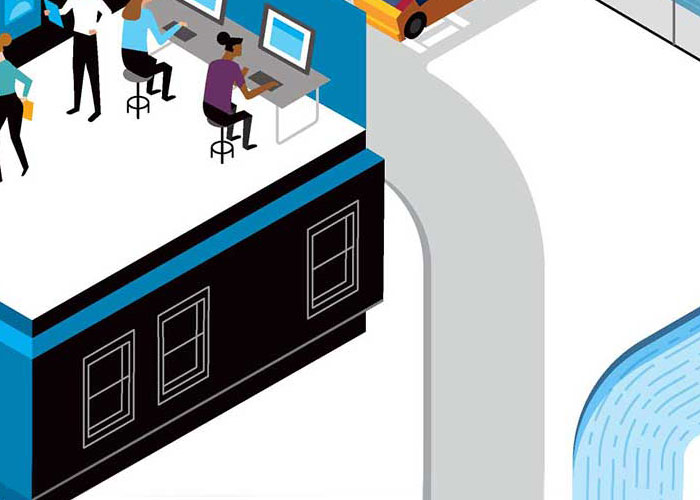

Preventing hackers from stealing trade secrets and selling info to competing companies and nations.
Preventing malware from stealing banking app credentials.
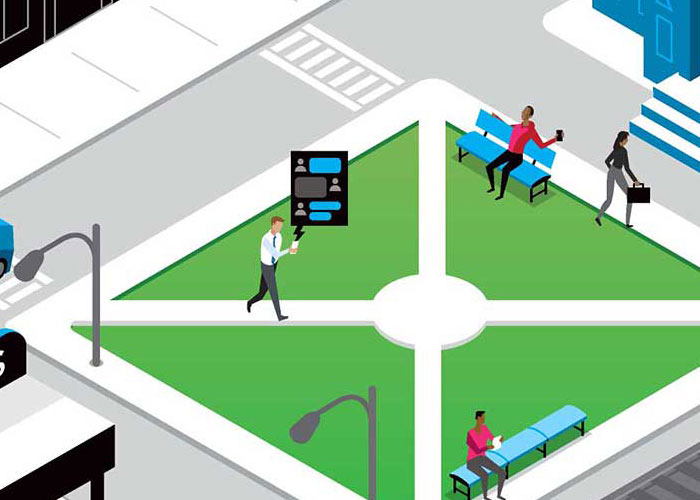

Preventing thieves from breaching cell networks and accessing private messages.
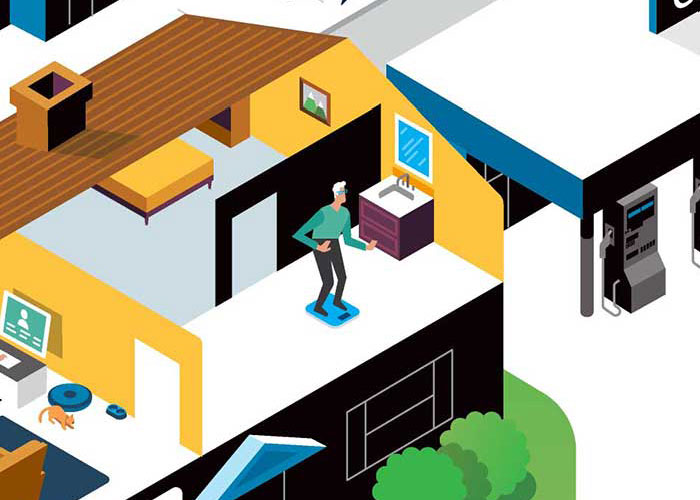

Preventing interception of sensitive health information.

Preventing thieves from skimming credit card information.
Protecting misplaced laptops from unauthorized access by identity thieves.
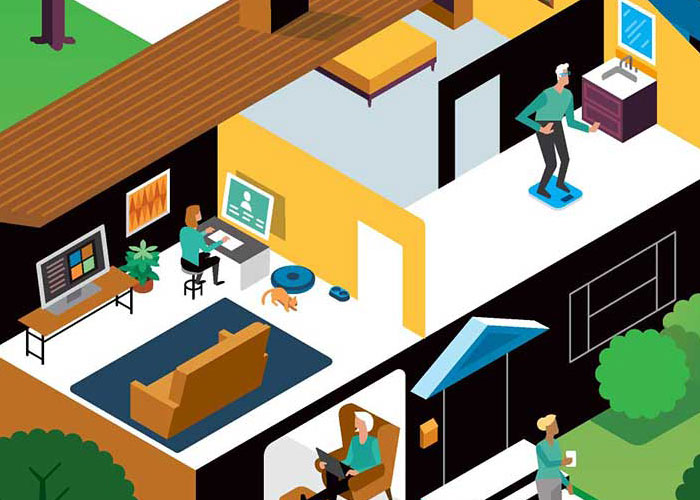

Protecting social media accounts from impersonation, blackmail, and ransom schemes.
Preventing apps from leaking personal health information.

Preventing attackers from commanding insulin pumps to administer an overdose.

Preventing criminals from breaching school systems, imperiling school funding, and exposing children’s data.

Preventing foreign adversaries from stealing sensitive military technologies.

Protecting overseas troops from foreign surveillance and targeted assaults.

Preventing criminals from modifying voter registrations and votes.

Protecting sensitive government personnel data about trusted officials.

Protecting lawmakers’ and candidates’ emails from leaks and forgery.

Preventing foreign adversaries from accessing and mapping critical infrastructure.

Protecting SCADA systems from unauthorized control and preventing service disruptions and injuries.

Protecting nuclear centrifuge equipment from computer viruses and foreign control.